Business & Finance
- Super User
- Category: Business & Finance
- Wednesday, 14 September 2016 08:13
Britain’s New 5-Pound Note is chewable, washable and harder to fake...
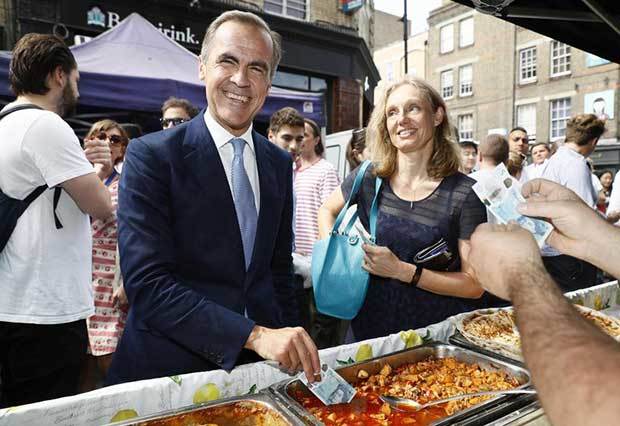 Mark Carney, governor of the bank of England, tests a new polymer £5 note by dipping it in a tray of food
Mark Carney, governor of the bank of England, tests a new polymer £5 note by dipping it in a tray of food
LONDON — It can withstand a spin cycle in a washing machine filled with extremely hot water. It can be eaten by mischievous toddlers or pet hamsters without causing lethal indigestion. It can fend off wily criminals with tiny lettering visible only under a microscope.
Printed for more than a hundred years on cotton paper, the 5pound note now comes in polymer, a thin, flexible plastic film that makes it stronger, safer and more resistant to counterfeiters. The British central bank introduced the new bill on Tuesday.
Britain is the latest country to choose polymer over paper for those hardy attributes, following Australia, Canada, Mexico, New Zealand and Singapore.
Given its durability, polymer is considered more environmentally friendly than traditional paper bills. The fiver, British slang for a £5 note, is expected to last about two and a half times as long as the current generation of paper notes.
The see-through windows on the £5 notes are difficult to replicate, enhancing the counterfeit protection. The bills are also cleaner since polymer doesn’t get soggy and is more resistant to dirt than paper.
“The use of polymer means it can better withstand being repeatedly folded into wallets or scrunched up inside pockets,” said Mark Carney, the governor of the Bank of England.
The polymer notes, featuring the former Prime Minister Winston Churchill, went through rigorous testing.The Bank of England stuffed them in jean pockets in washing machines with water at 40 degrees Celsius, or 104 degrees Fahrenheit, and put them in large spinning vessels filled with grime and dirt.
To help fend off counterfeiters, the central bank added special new features. A silver foil patch at the bottom of Big Ben on the note has a hologram of the word “Five” that changes to the word “Pounds.”
The person leading the effort is Victoria Cleland, 46, the bank’s chief cashier, whose signature is on every new £5 note. (She said she signed her name carefully and neatly.) Ms. Cleland, who studied philosophy, politics and economics at Oxford before getting her M.B.A., said the polymer notes, post spin cycle, had proved far sturdier than their paper counterparts.
“The paper notes get quite soggy and disintegrate, whereas the polymer notes retain their shape and don’t get crumpled,” she said in a telephone interview. Last year, 21,745 notes of all denominations were returned as mutilated, the central bank said.
She said the notes had also been carefully tested in the laboratory by health and safety experts to assure that pets or children accidentally chewing on them would not become ill. “A number of notes get returned each year and are chewed by pets, including parrots,” she said, before quickly adding: “We wouldn’t encourage people
to swallow the notes.”
Bank notes are important symbols of national identity. And the decision three years ago to replace the social reformer Elizabeth Fry with Churchill spurred some loud protests, since the queen would be left as the only female figure on British currency.
After the dissent, the bank decided to introduce a polymer £10note featuring the author Jane Austen, who will replace the scientist Charles Darwin when that note is introduced next summer.
The choice was a sign of “sense and sensibility,” the former chancellor of the Exchequer George Osborne wrote on Twitter at the time.
On Tuesday, Mr. Carney extolled Churchill as “one of the greatest statesmen of all time.” When Mr. Carney’s predecessor, Sir Mervyn King, first announced plans for the new Churchill note three years ago, he mused that the new £5 notes could be eventually referred to as “Winstons” and said it was appropriate that Churchill should be on “what is probably our most popular note.” Churchill’s words — “I have nothing to offer but blood, toil, tears and sweat” — appear on the bill.
The Bank of England has featured leading British luminaries on its notes for more than four decades; William Shakespeare, Charles Dickens, Adam Smith and Florence Nightingale have all graced bills.
The public makes nominations, and previous suggestions have included Princess Diana, David Bowie and David Beckham. (The famed soccer player was automatically excluded because a crucial criteria is being dead, the bank explained.)
While they may prove longer lasting, the new notes won’t go as far these days. After Britain’s vote this summer to leave the European Union, the pound has weakened. When the bills went into circulation on Tuesday in England and Wales, £5 was worth about $6.64, down from $7.70 about a year ago. Ms. Cleland said she used her first £5 polymer note Tuesday morning. She bought a cup of tea.
Correction: September 13, 2016
An earlier version of this article misstated the given name of a former chancellor of the Exchequer. He is George Osborne, not Charles.
A version of this article appears in print on September 14, 2016, on page B2 of the New York edition with the headline: New FivePound Note Is Chewable, Washable and Harder to Fake.
SOURCE: Newyork Times (nytimes.com)